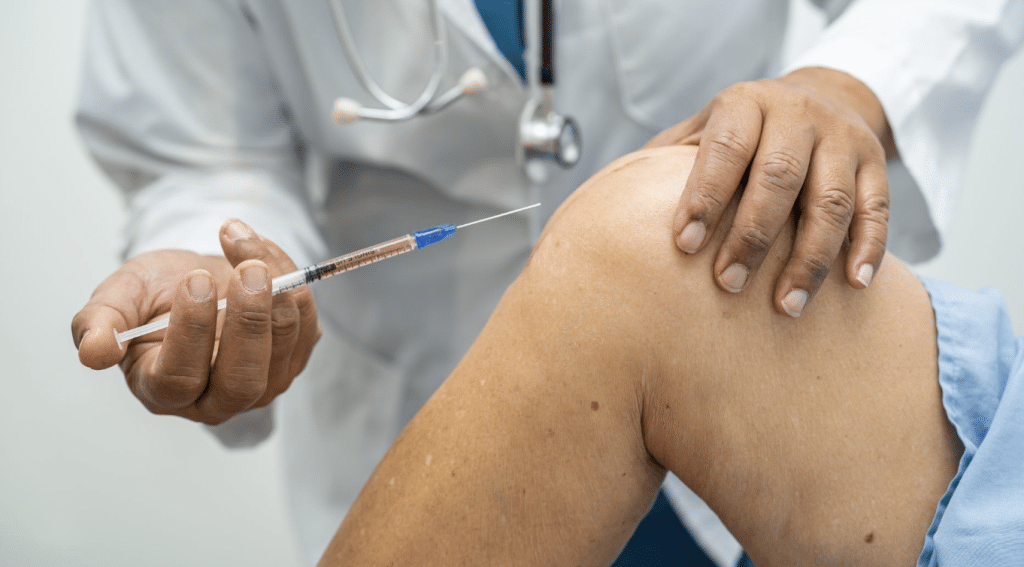
Osteoarthritis (OA) affects millions in the United States, with the knee being at risk the most when it comes to this disease. Viscosupplementation offers relief as an alternative to traditional treatments.
One such option is Durolane, a hyaluronic acid-based injection that provides long-lasting pain relief and protection for mild to moderate knee OA. However, like all treatments, Durolane can also have side effects that patients should be aware of.
In this article, we will discuss the short and long-term side effects of Durolane, providing insights into what patients can expect during and after treatment.
Key Takeaways
- Durolane, a hyaluronic acid injection used for osteoarthritis, can have both short-term and long-term side effects.
- Short-term side effects include localized pain, swelling, and redness at the injection site, which typically resolves within a few days.
- Long-term side effects are rare but may include infections, allergic reactions, and potential joint damage.
- Medical professionals should monitor patients for signs of side effects and be prepared to manage and treat them effectively.
About: Medical Spa RX provides medical practices with premium products at the best prices. If you’re looking to buy Durolane for your practice, the sales representatives at Medical Spa RX can give you guidance.
Short-Term Side Effects of Durolane

Localized Pain
One common short-term side effect of Durolane injections is localized pain at the injection site. This discomfort typically occurs immediately after the injection and can last a few hours to a few days. It is a normal reaction as the body adjusts to the hyaluronic acid introduced into the joint.
Most patients experience mild to moderate pain, which can be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers.
Swelling at the Injection Site
Swelling is another frequent side effect following Durolane knee injections. The knee joint area may become swollen as the body reacts to the injection. This swelling usually subsides within a few days. Applying ice packs to the affected area and keeping the leg elevated can help reduce swelling and provide relief.
Redness at the Injection Site
Redness at the injection site is also commonly reported by patients after receiving Durolane. This redness is typically mild and temporary, fading away within a day or two. It’s part of the body’s inflammatory response to the injection and should not cause significant concern unless accompanied by severe pain or other symptoms of infection.
Proper aftercare and following the medical provider’s instructions can help manage these short-term side effects effectively, ensuring a smoother recovery and better overall experience with Durolane treatment.
Long-Term Side Effects of Durolane

Infections
Infections are a rare but serious risk associated with Durolane injections. While infections are uncommon, they can occur if bacteria enter the joint during injection. Symptoms to monitor include increased pain, swelling, redness, warmth at the injection site, fever, and chills. Early detection and treatment are crucial.
If an infection is suspected, patients should contact their healthcare provider immediately. Treatment typically involves antibiotics; surgical intervention may be necessary to clean the infected joint in severe cases.
Allergic Reactions

Potential allergic reactions to Durolane can occur, though they are rare. Symptoms of an allergic reaction include itching, rash, swelling, dizziness, and difficulty breathing. Patients should seek immediate medical attention if they experience any of these symptoms.
Managing allergic reactions involves reducing symptoms with antihistamines or corticosteroids. In severe cases, an epinephrine injection may be required to treat anaphylaxis.
Potential Joint Damage
There is a risk of potential joint damage with Durolane injections, mainly if the injections are not administered correctly or if the joint is overused following treatment. Signs of joint damage include persistent pain, decreased mobility, and abnormal joint function.
Medical professionals should closely monitor patients through follow-up appointments to detect early signs of joint damage. If joint damage is identified, treatment options may include physical therapy to strengthen the surrounding muscles, additional viscosupplementation, or, in severe cases, surgical interventions to repair or replace the damaged joint.
By understanding these long-term side effects and monitoring for symptoms, healthcare providers can help ensure patient safety and the effectiveness of Durolane treatment.
Clinical Data and Patient Case Studies

Durolane is primarily used for patients with knee osteoarthritis (OA) who don’t find sufficient pain relief from conservative therapies. Common side effects include pain at the injection site, joint swelling, and joint pain.
Clinical studies conducted in the People’s Republic of China (PRC) reported adverse events associated with Durolane treatment. These included injection site pain (2.3%), joint swelling (1.7%), and joint pain (8.6%). Notably, these rates were comparable to a control group treated with a commercially available 5-injection sodium hyaluronate, and most reactions were mild to moderate.
For medical professionals addressing Durolane side effects, several best practices are essential:
- Monitoring and Education: Educate patients about potential side effects and closely monitor them after injection to detect any adverse reactions promptly.
- Symptomatic Treatment: Manage mild to moderate side effects symptomatically, addressing pain, swelling, and stiffness as needed.
- Reporting and Follow-Up: Encourage patients to report any unusual symptoms. If side effects occur, promptly assess and manage them appropriately.
Conclusion
Durolane has its share of side effects, both short and long-term. Patients might deal with various issues, from localized pain to potential joint damage. Yet, knowing these can help manage and even prevent some problems.
Doctors play a significant role in monitoring symptoms and advising on the best care strategies. Understanding these side effects is critical to helping patients through their osteoarthritis treatment journey with Durolane.
FAQs
1. What is Durolane, and what are its short-term side effects?
Durolane is a medical treatment for joint pain, particularly in the knee. Short-term side effects can include minor discomfort at the injection site, swelling, or redness.
2. Are there any long-term side effects of using Durolane?
Long-term side effects are rare but may include more severe reactions such as allergic responses or infections. It’s important to discuss these potential risks with your healthcare provider.
3. Is it safe to use Durolane over an extended period?
Safety depends on individual health factors and response to treatment. Regular check-ins with your healthcare provider will help monitor any potential long-term impacts.
4. Can everyone use Durolane?
Not everyone should use Durolane. Individuals with certain allergies or infections may need alternative treatments. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting new treatments.
References
World Health Organization. (n.d.). Osteoarthritis. Retrieved July 9, 2024, from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/osteoarthritis
Leighton, R., Fitzpatrick, J., Smith, H., Crandall, D., Flannery, C. R., & Conrozier, T. (2018). Systematic clinical evidence review of NASHA (Durolane hyaluronic acid) for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis. Open access rheumatology : research and reviews, 10, 43–54. https://doi.org/10.2147/OARRR.S162127
Peck, J., Slovek, A., Miro, P., Vij, N., Traube, B., Lee, C., Berger, A. A., Kassem, H., Kaye, A. D., Sherman, W. F., & Abd-Elsayed, A. (2021). A Comprehensive Review of Viscosupplementation in Osteoarthritis of the Knee. Orthopedic reviews, 13(2), 25549. https://doi.org/10.52965/001c.25549