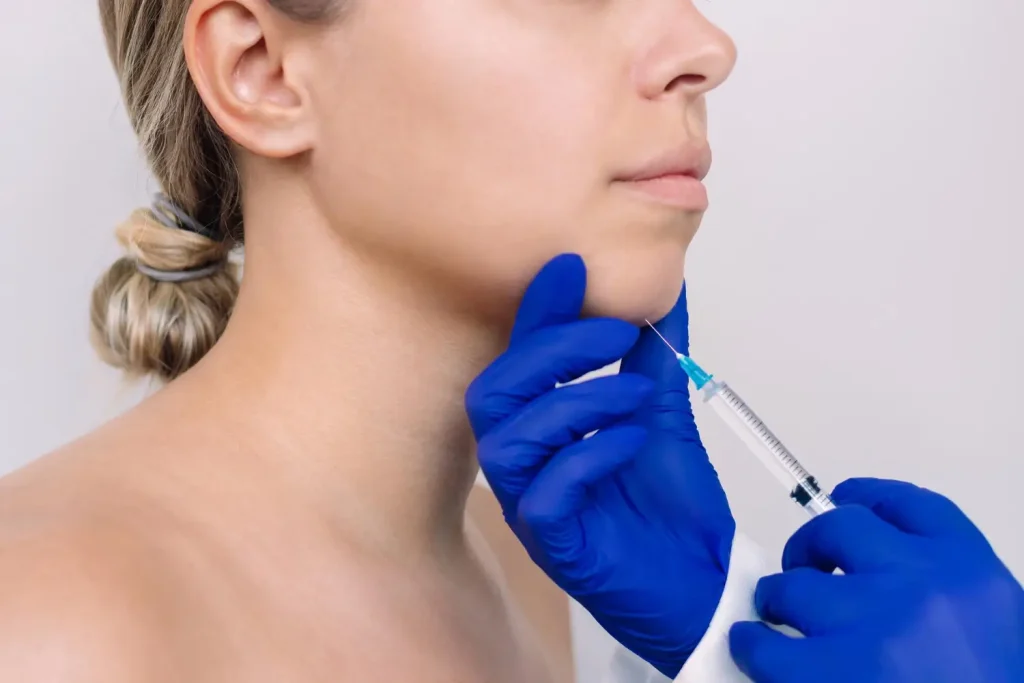
Excess visceral fat poses significant health risks, including elevated blood sugar, high blood pressure, and increased inflammation. Research shows that visceral fat is more metabolically active than subcutaneous fat, releasing inflammatory molecules that contribute to insulin resistance and cardiovascular disease.
For individuals seeking non-surgical solutions to reduce localized fat, Belkyra presents a breakthrough treatment specifically FDA-approved for the reduction of submental fat (fat beneath the chin). Its active ingredient, deoxycholic acid, works by destroying fat cells, which the body then eliminates naturally through the lymphatic system. This injectable procedure is clinically proven to contour the jawline and improve facial aesthetics.
In this article, we will explore the clinical evidence supporting Belkyra’s effectiveness in treating submental fat, its mechanism of action, and what patients can expect during and after treatment.
Key Takeaways
- Belkyra is only FDA-approved for reducing fat under the chin, not for use on the stomach area or other body parts.
- Using Belkyra for belly fat is off-label and lacks sufficient clinical research supporting its safety, efficacy, or long-term outcomes in that area.
- Deoxycholic acid, the active ingredient in Belkyra, dissolves fat cells which are gradually broken down and eliminated through the body’s natural processes.
- Treating larger areas like the abdomen may require significantly more product, increasing risks of swelling, bruising, and post-treatment discomfort.
- Belkyra treatments usually require multiple sessions spaced weeks apart, with gradual fat reduction becoming visible over time rather than immediately.
- A licensed provider can help determine if Belkyra or alternative non-surgical options like CoolSculpting or liposuction are better suited for belly fat.
About: Medical Spa RX provides medical practices with premium products at the best prices. If you’re looking to buy Belkyra (Kybella) wholesale for your practice, the sales representatives at Medical Spa RX can give you guidance.
Off-Label Use: Rationale and Clinical Context
Belkyra, marketed as Kybella in the United States, is an injectable treatment approved by the FDA specifically for reducing submental fat, commonly known as a double chin. However, growing interest in its fat-dissolving capabilities has prompted off-label exploration of Belkyra for other areas of stubborn fat accumulation—particularly abdominal fat.
The appeal lies in Belkyra’s active ingredient, deoxycholic acid, a naturally occurring bile acid responsible for breaking down dietary fats in the body. When injected into localized fat pockets, it disrupts adipocyte (fat cell) membranes, permanently destroying them. These lysed cells are then cleared through the body’s lymphatic system, resulting in fat volume reduction over time.
Because this mechanism is not site-specific, clinicians have begun exploring off-label use of Belkyra in areas beyond the submental region—such as the abdomen, bra line, jowls, and thighs. However, it is important to understand that such applications are not FDA-approved and lack standardized protocols regarding dosage, injection technique, and expected outcomes.
Review of Clinical Data and Efficacy Studies
The bulk of clinical data on Belkyra stems from its FDA trials targeting submental fat. Studies like the REFINE-1 and REFINE-2 trials demonstrated its efficacy in reducing double chin volume, with most patients showing visible improvement after two to four sessions.

In a 2022 study, participants who underwent Belkyra double chin treatment reported high satisfaction rates, with improved chin contour and psychological well-being. These results have led to its widespread adoption in aesthetic medicine for jawline contouring and facial balancing.
However, no large-scale, randomized controlled trials have been published for abdominal fat. Much of the support for its use in this area comes from case studies, small clinical trials, and practitioner-reported outcomes. Anecdotal evidence suggests that deoxycholic acid can reduce small, localized abdominal fat pads, but outcomes can vary significantly based on fat type, depth, and patient characteristics.
Until further studies confirm its efficacy, safety, and optimal injection protocols for belly fat, the use of Belkyra in this region remains investigational.
Patient Selection and Informed Consent for Off-Label Applications
Patient selection is critical when considering Belkyra for off-label areas such as the abdomen. Unlike the submental region, abdominal fat is often a mix of subcutaneous and visceral fat. Belkyra can only target subcutaneous fat, which lies just beneath the skin. Visceral fat surrounding internal organs remains unaffected and poses greater health risks.
Ideal candidates for off-label abdominal treatment include:
- Adults in good general health
- Individuals with localized, diet-resistant fat pockets
- Patients with realistic expectations who understand that multiple sessions may be needed
- Individuals not interested in or ineligible for surgical fat reduction options
It is imperative to conduct a thorough consultation, which should include:
- Explanation of the off-label status and lack of FDA approval for abdominal use
- Clarification of realistic outcomes and number of sessions likely required
- Full disclosure of potential side effects, complications, and limitations
- Documented informed consent, with signed acknowledgment of non-standard usage
Clear, empathetic communication not only protects practitioners legally but also builds patient trust and improves satisfaction.
Injection Techniques and Pharmacokinetic Considerations
Proper injection technique plays a vital role in achieving successful outcomes and minimizing risks. When adapting Belkyra for use on the abdomen, a few key adjustments must be made compared to its use under the chin.
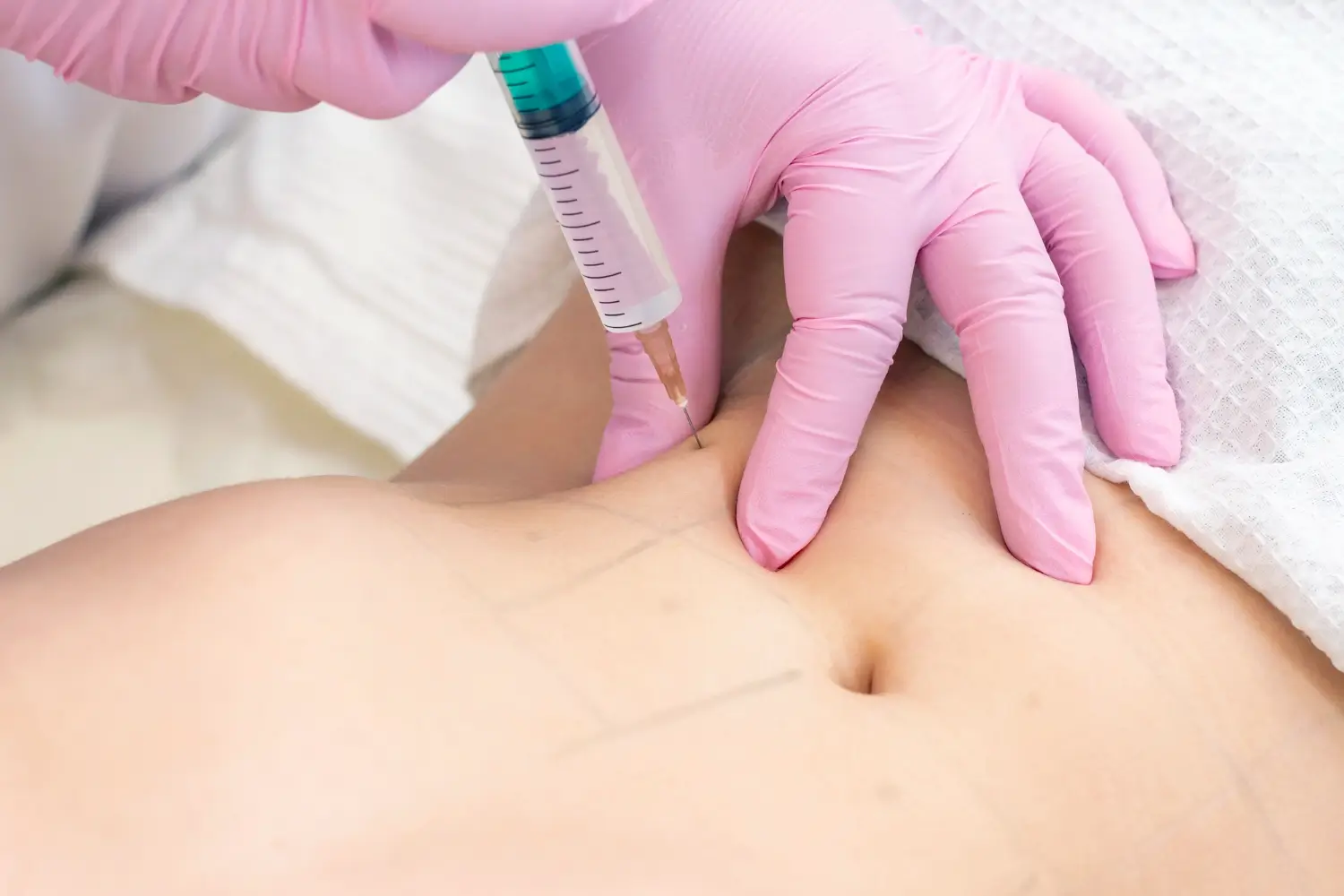
Some key technical considerations are:
- Injection Depth: Must reach subcutaneous fat without affecting muscle or deeper tissue
- Volume Per Session: Typically higher than submental treatments; must be adjusted per individual fat distribution
- Spacing and Grid: Multiple injection sites spaced evenly over the treatment area to ensure consistent results
- Avoiding Vital Structures: Extra caution is needed in the abdominal region due to the proximity of organs
Pharmacokinetics of deoxycholic acid may vary depending on fat density, circulation, and injection site. Some patients may exhibit greater inflammatory responses or slower absorption when treated on the abdomen, highlighting the need for individualized treatment plans.
Potential Risks, Adverse Events, and Future Research
Though generally well-tolerated in submental applications, using Belkyra on the abdomen (belly fat) introduces greater risk due to the size and complexity of the area. Documented risks include:
- Swelling and Bruising: Common and expected, though more pronounced than in facial areas
- Pain and Tenderness: Often more intense due to larger treatment zones
- Hard Nodules: Resulting from inflammatory response or fibrosis
- Skin Necrosis: If injected too superficially or into vascularized areas
- Nerve Injury: Particularly if anatomical landmarks are misjudged
- Infection: Especially if post-treatment care is neglected
The lack of regulatory oversight in off-label uses means there is no universal dosing or technique standard, increasing variability in outcomes.
Future Research Needs
- Randomized clinical trials assessing safety and efficacy for abdominal fat
- Standardized injection techniques and dosing guidelines
- Long-term safety monitoring and follow-up protocols
- Patient-reported outcomes comparing Belkyra to other non-invasive fat-reduction methods
Conclusion
Belkyra remains an FDA-approved, non-surgical treatment with a proven track record in submental fat reduction. Its off-label use for abdominal fat is an emerging trend, driven by patient demand and clinical curiosity, but it should be approached with caution.
Until robust clinical evidence is available, patient safety must take precedence. This means careful candidate selection, transparent communication, precise injection technique, and strict post-care protocols. By following these standards, providers can responsibly explore the broader potential of Belkyra while maintaining high ethical and clinical standards.
FAQs
1. What is Belkyra?
Belkyra is an injectable treatment containing deoxycholic acid to destroy fat cells under the chin.
2. How long do Belkyra results last?
Results are typically long-lasting since treated fat cells are permanently destroyed, though weight gain may affect outcomes.
3. How many sessions are required?
Most patients need 2 to 4 sessions about 4 to 6 weeks apart. Depending on fat volume, some may need more.
4. What are the common side effects of Belkyra?
Common side effects include swelling, bruising, pain, and temporary discomfort at the injection site. These typically resolve within a few days to weeks.
5. Is Belkyra safe?
Belkyra is generally safe as long as a qualified healthcare professional administers the treatment. However, as with any medical procedure, patients should anticipate some risks or side effects.
6. Who is a good candidate for Belkyra?
Ideal candidates have moderate to severe submental fullness and are bothered by it. They should consult with a healthcare provider to determine suitability.
References
Salvador L, Benito-Ruiz J. Safety and efficacy of deoxycholic acid injection for hypogastric fat reduction: a pilot study. Dermatologic Surgery. 2021;47(4):e132-e137. doi:10.1097/dss.0000000000002823
Metzger KC, Crowley EL, Kadlubowska D, Gooderham MJ. Uncommon adverse effects of deoxycholic acid injection for submental fullness: Beyond the clinical trials. Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery. 2020;24(6):619-624. doi:10.1177/1203475420943270
Kelm RC, Ibrahim O. Update on expanded use of Kybella. Advances in Cosmetic Surgery. 2022;5(1):99-112. doi:10.1016/j.yacs.2021.12.008
Liu M, Chesnut C, Lask G. Overview of Kybella (Deoxycholic acid injection) as a fat resorption product for submental fat. Facial Plastic Surgery. 2019;35(03):274-277. doi:10.1055/s-0039-1688943