According to the Mayo Clinic, Botox injections offer cosmetic benefits and are also used in medical settings to help alleviate symptoms of various health conditions, including chronic migraine headaches. This approach is capable of significantly relieving those experiencing headaches 15 or more days a month.
The procedure involves blocking nerve chemical signals that cause muscles to contract, which helps manage pain and minimize headaches. Through professional insight and scientific exploration, Botox extends beyond its cosmetic uses and effectively reduces headache frequency and severity.
In this article, readers will learn about the details of Botox treatment for tension headaches, from the science behind its efficacy to practical considerations and patient testimonials.
Key Takeaways
- Botox injections can alleviate symptoms of chronic tension headaches, especially in those experiencing headaches 15 or more days a month, by blocking nerve signals that cause muscle contractions.
- Chronic tension headaches, characterized by dull, aching head pain and tightness across the forehead or back, significantly impact the quality of life and job productivity.
- Botox’s effectiveness for chronic tension headaches involves a complex interaction with the body’s pain pathways, including modulating neurotransmitter release and enhancing opioidergic transmission.
- Preparing for Botox treatment involves selecting a qualified healthcare provider and discussing treatment expectations and potential side effects.
- Common side effects of Botox for tension headaches include localized swelling, neck pain, and mild muscle weakness, with some individuals (e.g., pregnant women and those with cow’s milk protein allergy) advised to avoid this treatment.
Understanding Chronic Tension Headaches
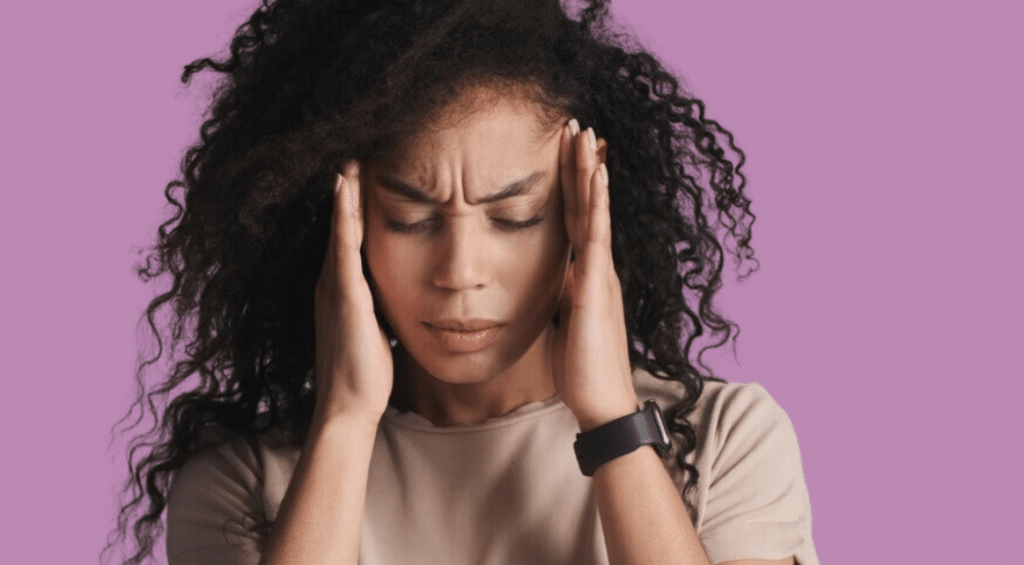

Symptoms and Triggers
Chronic tension headaches are characterized by a dull, aching head pain accompanied by a feeling of tightness or pressure across the forehead or on the sides and back of the head. People may also experience tenderness in the scalp, neck, and shoulder muscles. These headaches can become chronic if they occur 15 or more days a month for at least three months.
Unlike migraines, tension-type headaches usually aren’t associated with visual disturbances, nausea, or vomiting, and physical activity doesn’t typically affect the pain. Stress is the most commonly reported trigger for these headaches, and due to their frequency and the discomfort they cause, they can significantly impact quality of life.
Impact on Quality of Life
Chronic tension headaches and how Botox works for migraines can severely impact job productivity and overall quality of life. The constant pain from these headaches makes it difficult for individuals to engage in work or social activities, resulting in decreased functioning and diminished quality of life.
Regular exercise and stress management techniques, such as biofeedback training, cognitive behavioral therapy, and other relaxation methods, can help prevent tension-type headaches. Understanding the mechanism of how Botox works for migraines offers additional insight into its potential benefits for those suffering from chronic tension headaches.
Botox: An Overview
What Is Botox?
Botox, a brand name for botulinum toxin, is a neurotoxic protein produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. It is widely known for its cosmetic use in reducing facial wrinkles. However, it also has various medical applications, including treating chronic tension headaches.
How Botox Works in Medical Treatments
Is Botox or fillers better? Botox works by blocking the release of certain nervous system chemicals involved in pain transmission. This effectively reduces the activity of the muscles and nerves contributing to the headache, decreasing the frequency and severity of headache episodes. The treatment involves injections of Botox into specific areas, and its effects can last for several months.
Botox for Headache Treatment
The Mechanism Behind Botox for Headaches
Botox’s effectiveness in treating chronic migraine headaches may be attributed to its action beyond the injection site, including axonal transport to anatomically connected sites. It is believed to modulate neurotransmitter release, alter the surface expression of receptors and cytokines, and enhance opioidergic transmission. These mechanisms suggest a complex interaction with the body’s pain pathways.
Clinical Studies and Efficacy
Clinical and experimental research over the past decade has deepened our understanding of how Botox works for headaches, suggesting it could be a viable alternative for patients not responding to other treatments. However, further studies are encouraged to fully grasp its benefits and mechanisms in headache and pain management.
Preparing for Botox Treatment
Selecting the Right Healthcare Provider
Choosing a healthcare provider skilled in Botox treatments for headaches is vital. Their qualifications and experience are fundamental to ensuring your treatment is customized to your needs, maximizing safety and effectiveness. Engaging with a specialist familiar with Botox’s application for headaches will provide you with tailored advice and ensure your treatment plan is optimal for your specific situation.
What to Discuss During Your Consultation
During your consultation, discuss your headache history, treatment expectations, and any potential side effects of Botox. It’s also an excellent time to ask about the procedure’s details, including its performance and what results to anticipate.
The Treatment Process
What to Expect During the Botox Procedure
The Botox procedure for treating chronic tension headaches involves injecting botulinum toxin into specific areas around the head, face, and neck. These areas often include the forehead, temples, and the back of the head and neck, targeting the tiny muscles under your skin.
The treatment is performed using a small needle, and sometimes “trigger points” where the headache pain originates are specifically targeted. This process is tailored to respect patients’ unique anatomy and pain points. It may take several weeks and possibly more than one set of injections before patients start experiencing relief from their migraines.
Post-Treatment Care and Follow-Up
After receiving Botox injections for tension headaches, it’s common to experience localized swelling, neck pain, and mild muscle weakness. The procedure is considered safe and effective when administered by qualified professionals. It’s essential to follow the healthcare provider’s instructions for post-treatment care and attend follow-up appointments to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment and adjust as needed.
Benefits of Botox for Chronic Tension Headaches
Symptom Relief and Duration
Botox alleviates tension headaches by preventing muscle contractions and reducing headache frequency. Its mechanism of action includes:
- inhibiting the release of acetylcholine
- stopping muscle spasms
- blocking substance P, a chemical that heightens pain sensitivity
For many patients, Botox injections can effectively reduce the frequency of headaches in those with chronic migraine. They can also lessen severe symptoms associated with these migraines.
Quality of Life Improvements
Chronic tension-type headaches, while not as debilitating as migraines, can significantly impact one’s quality of life. Botox offers a treatment option for those whose headaches do not respond to medication, providing pain relief. Botox can offer significant relief by addressing the root causes of tension headaches, including muscle contractions in the neck and head.
Potential Side Effects and Considerations
Common Side Effects
When receiving Botox injections for chronic tension headaches, some common side effects you might experience include:
- Localized swelling
- Neck pain
- Mild muscle weakness
- Headache or flu-like symptoms
- Dry or watering eye
- Drooping eyelid, eyebrow, or side of the mouth
- Drooling
These side effects are generally temporary, but monitoring and reporting any persisting or worsening conditions to your healthcare provideris essential.
Who Should Avoid Botox for Headaches
Botox treatments for chronic tension headaches may not be suitable for everyone, including:
- Pregnant women and nursing mothers, due to the lack of research on the effects on fetal and infant health.
- Individuals with an allergy to cow’s milk protein could trigger an allergic reaction.
- People experiencing any of the following rare but severe symptoms after Botox injections should seek immediate medical attention:
- Vision problems
- Muscle weakness
- Trouble speaking or swallowing
- Inability to control the bladder
- Difficulty breathing
It’s crucial to have a thorough consultation with a healthcare provider to discuss medical history and potential risks before deciding on Botox as a treatment option for headaches.
Conclusion
Botox offers a promising treatment option for individuals suffering from chronic tension headaches, extending beyond its cosmetic applications to provide significant relief from debilitating symptoms. With proper medical guidance and consideration of potential side effects, Botox can improve the quality of life for those who have not found relief through traditional headache medications.
FAQs
- How does Botox help with chronic tension headaches?
Botox helps by blocking the release of chemicals involved in pain transmission, reducing muscle and nerve activity that contribute to headaches, and decreasing their frequency and severity.
- Are there any side effects of using Botox for tension headaches?
Typical side effects include localized swelling, neck pain, mild muscle weakness, and occasionally, flu-like symptoms, but these are generally temporary.
- Who should avoid Botox treatments for headaches?
Pregnant women, nursing mothers, individuals allergic to cow’s milk protein, and those experiencing severe symptoms like vision problems or muscle weakness post-injection should avoid Botox for headaches.
- How often do I need to get Botox injections for chronic tension headaches?
The frequency of Botox injections varies among individuals, but the effects can last several months. Your healthcare provider will determine the optimal schedule based on your response to the treatment.
- Can Botox injections cure my chronic tension headaches?
While Botox injections can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of chronic tension headaches, they are considered a treatment rather than a cure, aiming to manage symptoms effectively.
References
Weiss, C. (2022, September 18). Mayo Clinic Q and A: Botox for migraines. Mayo Clinic News Network. Retrieved from https://newsnetwork.mayoclinic.org/discussion/mayo-clinic-q-and-a-botox-for-migraines/
Mayo Clinic Staff. (2023, March 10). Botox injections. Mayo Clinic. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/botox/about/pac-20384658
Johns Hopkins Medicine. (n.d.). Botulinum toxin injectables for migraines. Retrieved from https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/botulinum-toxin-injectables-for-migraines
Do, T. P., Hvedstrup, J., & Schytz, H. W. (2018). Botulinum toxin: A review of the mode of action in migraine. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica, 137(5), 442–451. https://doi.org/10.1111/ane.12917
Patient.info. (n.d.). Chronic tension headache. Retrieved from https://patient.info/brain-nerves/headache-leaflet/chronic-tension-headache
Mayo Clinic Staff. (2023, September 26). Tension headache. Mayo Clinic. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/tension-headache/symptoms-causes/syc-20353977